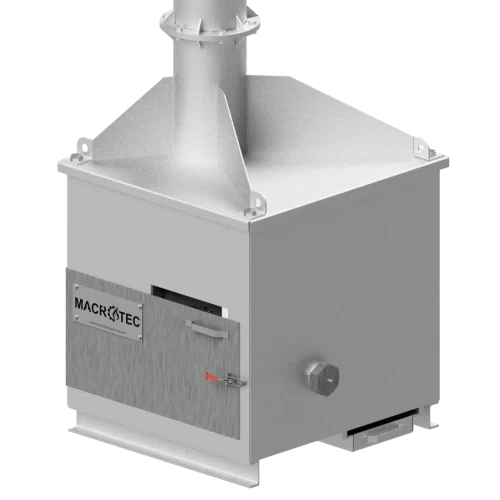
Incinerators
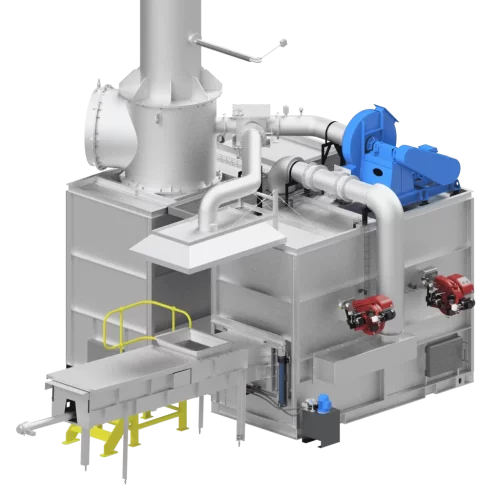
Macrotec designs and manufactures the most advanced incinerators on the market, incorporating cutting edge design of the combustion chambers and combustion air to ensure complete combustion, Oxygen analysers for combustion control, manual or auto feeders, and world leading flue gas abatements systems.
Our incinerators cater for various applications and conditions. Our focus has always been on hazardous waste types, such as animal, medical, biological, mining, and pharmaceutical waste, along with waste generated by remote operations such as hotels and military operations.
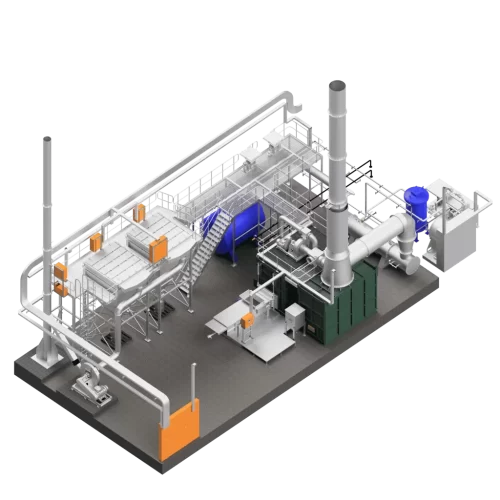
Our incinerator are available in three main configurations, Biomass, Standalone, and Incinerators with Air Pollution Control. This provides a solution for most sites and clients, from basic incinerators to incinerator plants for centralised waste treatment.
Our innovative solution for rural areas that don’t have a reliable supply of fuel, these incinerators use biomass to heat up and maintain the required temperature.
Our standard incinerators that are used all over the world. These incinerators offer reliability, easy maintenance, low emissions, various feeding systems, and can handle multiple waste types.
Our solution for ultra-low emissions, these incinerators are integrated with dry gas scrubbing, flue gas filtration, and heat recovery. These plants comply with EU and South African emission regulations.
A few of our clients






Emissions Compliant
Our Incinerators with Air Pollution Control (APC) are compliant to important regulatory standards, such as the EU Incinerator Directive and the South African Emission Regulations.
Certification
Macrotec is certified to the following standards:
ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems
ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management Systems
ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational Health & Safety Management
Quality
Our objective is to design and manufacture Quality Incinerators, that are robust, easy to operate, and with low maintenance requirements. Our manufacturing involves a strict Quality Control Procedure, with multiple inspections to ensure the highest quality product. Our factory is also certified to ISO 3834.

Design Highlights
Refractory
We utilise a high-quality refractory that has been designed specifically for the harsh conditions that incinerators face. This refractory is chemically resistant to both alkali and acidic substances, as well as having the physical properties to produce a high abrasion resistance. Unlike other refractories, ours has an extremely wide temperature range for operation – it comfortably accommodates the incinerator temperature ranges typically encountered in incinerators. For most incinerator models we also cast the refractory in sections, allowing for expansion joints, to increase the refractory operating life.
Insulation
We use high quality insulation, with a low thermal conductivity, to achieve safe working surface temperatures and minimal heat loss.
3CR12 Stack
We provide an optional 3CR12 stack as opposed to a mild steel stack for added corrosion resistance.
Oxygen Analyser
A fast response oxygen analyser is installed for combustion control. This allows for careful control of combustion air, increasing and decreasing the combustion fan speed as conditions inside the incinerator change. This leads to a dramatic decrease in emissions. Also, when the Oxygen demand decreases, the combustion fan speed also decreases, saving fuel and electricity.
Fuel Consumption
Due to the thermal properties of our refractory and insulation, and with the careful combustion air control, we achieve industry leading fuel usage.
Chamber Sizes
Combustion volume is one of the most important factors affecting incinerator emissions. This is because it sets the retention time for flue gas, which influences the extent of combustion achieved, and serves as a settling chamber for particulate matter, to ensure cleaner emissions. Our incinerators have larger combustion chambers relative to competitors for a given processing capacity. This ensures a longer reaction time, better combustion, and lower emissions.
Stack Design Code
All our stacks are designed according to ASME STS-1.
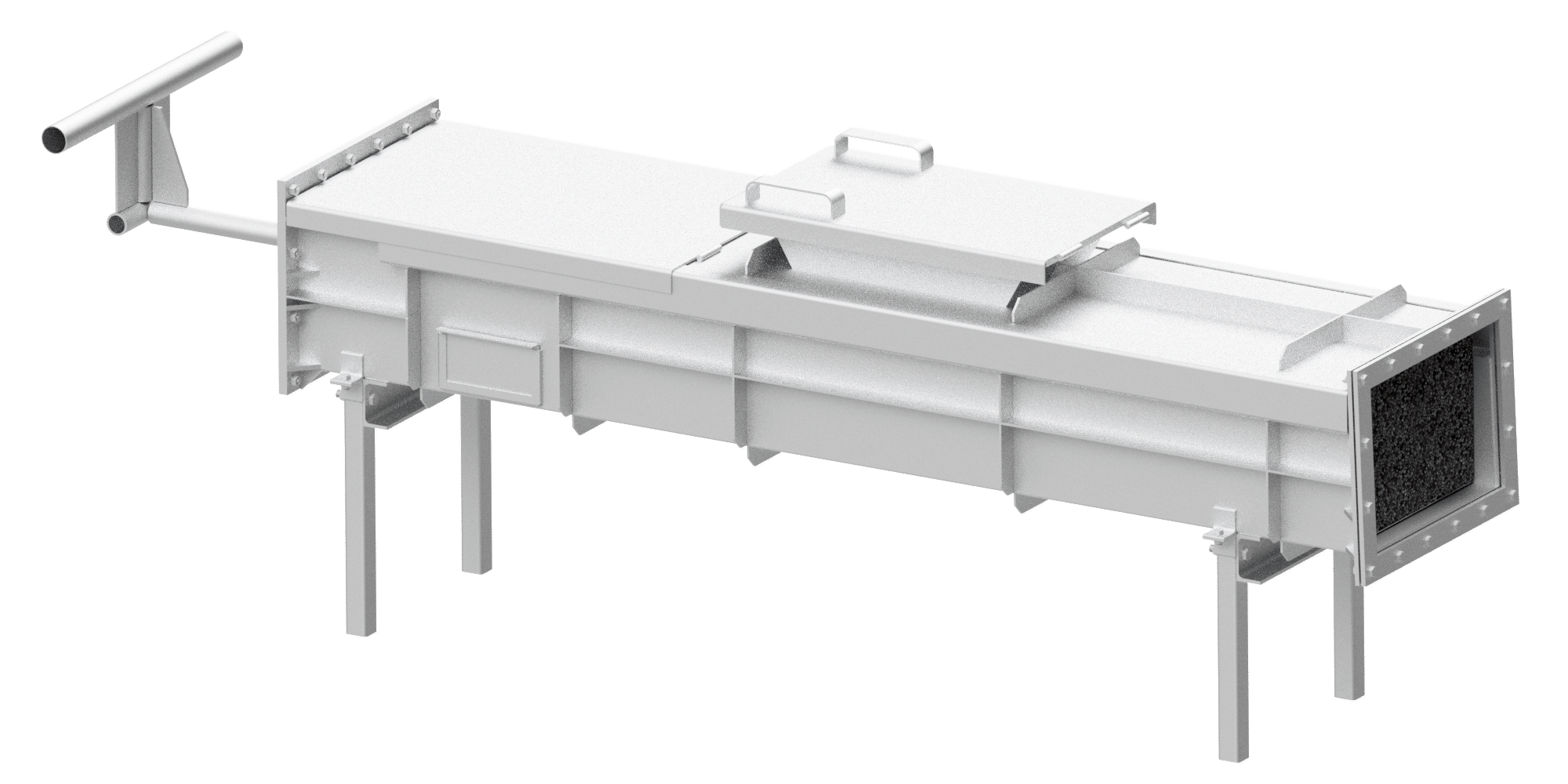
Manual Feeders
Our incinerator manual feeders offer a cost-effective option to minimise waste handling and to improve operator health and safety. The manual feeder has a manual push system to inject waste into the incinerator, minimising the exposure of operators to incinerator heat and physically handling the waste.
Auto Feeders
Our auto feeders offer the most advanced incinerator feeding system available. The feeder integrates a bin-tipper or manual loading of waste into a hopper, with hydraulics opening the incinerator gate and pushing the waste into the incinerator. The air sealed incinerator gate prevents air in-leakage, and thereby enhancing combustion conditions. Various safety systems are included to ensure safe operation. The auto feeder also automates when waste is pushed into the incinerator, optimising incinerator loading, reducing emissions, and removing operator error.
Continuous Feeding
Our incinerators are continuous feeding, and not batch loaded. This has two main advantages:
- Continuous feeding allows for more effective combustion control and better emissions as the spikes in heat and flue gas associated with batch feeding can be avoided.
- The incinerator is also de-ashed continuously, without needing to switch off and stop operations. This saves time and fuel, as the incinerator is not pre-heated again between batches.
Access Doors
Access doors are easy to open and well insulated, allowing for easy inspection and maintenance.
Easy Operations and Maintenance
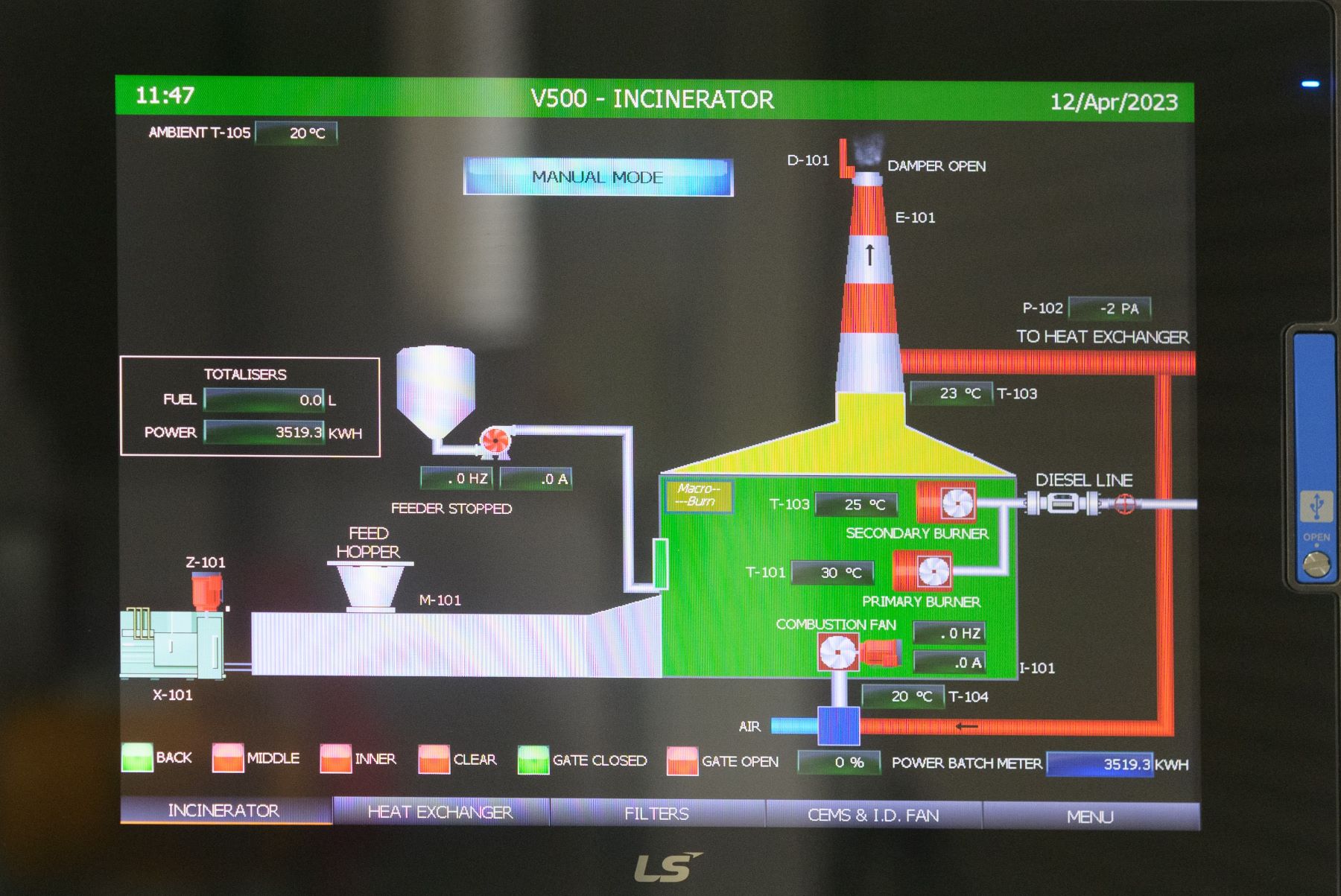
Our incinerators are designed to allow for easy operability when it comes to feeding, stoking and ash removal. Our main doors are large enough to allow for the easy inspections and access for maintenance when required. Our HMI provides clear and concise instructions to the operator with regards to temperature, hours until next service, and error explanations.
Easy diagnostics
Our HMI screens provide clear and easy to understand error messages, along with complete performance and error logs to enable operators or maintenance staff to diagnose issues.
Performance and compliance
Logs are stored for up to 360 days on the following metrics to assist with Quality Control and Regulatory Compliance:
- Temperature
- Start / Stop times
- Errors
User Security
We provide multiple user levels on the Control System, with tailored permissions:
• Operators
• Site Engineers
What You Need to Know About Incineration
Incineration is a method of waste management employed to process various types of wastes including municipal, biosolids, hazardous, non-hazardous industrial, medical, as well as other liquid residues and potentially harmful gases. Through this method, wastes are transformed into flue gas, ash, and heat. The resulting ash predominantly consists of non-combustible inorganic substances.
Incineration offers the following potential advantages:
- Volume reduction
- Detoxification
- Environmental impact mitigation
- Regulatory compliance
- Energy recovery
- Stabilization in landfills
- Detoxification and sterilization
It’s essential to understand that only substances that can burn will undergo incineration. Non-combustible materials will end up as either ash or flue gas, depending on their boiling points.
- Municipal solid waste (MSW)
- Industrial waste
- Medical waste
- Animal carcasses and animal waste
- Hazardous waste
- Food waste
- Glass
- Metal
- Sand
- Stones
- Concrete and Bricks
Sizing an Incinerator
Different waste types will also burn at different rates, and thus affect the actual incinerator throughput. This is an important consideration to keep in mind when sizing an incinerator. When trying to determine the required incinerator size, we usually work backwards by determining:
- How much waste will be produced per month?
- What is the composition of this waste?
- How many days per week, and hours per day, will we be operating?
- What is the altitude of the site?
After determining the above, we can work out the incinerator throughput requirement, by considering the rate at which different waste will burn. The factors that influence this are:
- Nett calorific value (CV) of the waste
- Moisture content of the waste
- Density of the waste
- How the waste is packaged
Incinerator Air Pollution Control
Incinerator emissions has become a major issue around the world. We incorporate several technologies to reduce emissions on all our incinerators, but depending on your location and waste being incinerated, more advanced Air Pollution Control might be required, such as:
- Wet Scrubbing
- Dry Gas Scrubbing – Absorption (for acid gasses) & Adsorption (for heavy metals and Dioxins)
- Bag Filtration
- Ceramic Filtration
Other Considerations
- Where will waste be stored before incineration?
- How will waste be moved from storage to the incinerator?
- Will a shredder be required?
- Is a manual or auto feeder required?
- What auxiliary fuel will be used, LFO (diesel), LPG, Natural Gas, or Dual fuels?
- Is there a requirement to burn waste oil?
- What is the plantroom ventilation requirement?
Related Incinerator news articles
What is Incineration?
What is Incineration? Incineration is a waste management technique used to treat municipal, biosolids, hazardous and non-hazardous industrial and medical wastes, and other liquids, residues, and toxic and flammable gases […]

What Types of Waste can be Incinerated?
What Types of Waste can be Incinerated? Waste management is a major challenge facing communities worldwide. As populations continue to grow and consumption patterns change, finding sustainable ways to manage […]

What Types of Waste cannot be Incinerated?
What Types of Waste cannot be Incinerated? An Incinerator is a furnace used to combust waste materials. Incineration is a popular waste management method where materials are burnt at high […]

Incinerator Air Pollution Abatement
Incinerator Air Pollution Control (APC) Air pollutant emissions have become the focus of public concern and regulatory scrutiny regarding incineration facilities. The fraction of total facility capital cost for system […]

How Does an Incinerator Work?
How does an incinerator work? Introduction In an era of growing concern for environmental sustainability, the process of incineration has gained renewed attention as a potential solution for managing waste, […]